Don't join any of these group ISIS, Al Qaida, Al Shabab and Boko haram these are human traffickers
Wednesday, April 26, 2017
Tuesday, April 25, 2017
Mission Unaccomplished, 15 Years Later
Originally posted at TomDispatch.
If you’re going to surround yourself with generals in the Oval Office, as Donald Trump has done, that means one thing in these years: you’re going to appoint men whose careers were made (or unmade) by what was once known as the Global War on Terror. They will be deeply associated with Washington’s 15 years of disastrous wars and conflicts in the Greater Middle East, which have left that region a set of failed or near-failed states and a hotbed of terror outfits, including various branches of al-Qaeda and the Islamic State. Secretary of Defense James “Mad Dog” Mattis, for instance, led troops in the initial post-invasion period in Afghanistan in 2001; in the taking of the Iraqi capital, Baghdad, in 2003; in the fierce fighting for the city of Fallujah in 2004; and then, from 2010 to 2013, he was in charge of U.S. Central Command (CENTCOM), with responsibility for the Greater Middle East. In that post, he cooked up a scheme to take out either an Iranian oil refinery or power plant in the “dead of night,” an act of war meant to pay that country back for supplying mortars to Iraqi insurgents killing American troops. That plan, nixed by the Obama White House, seems to have played a role in his removal from the CENTCOM post five months early.
General John Kelly, head of the Department of Homeland Security, also commanded troops and fought in Iraq. (His son was killed in Afghanistan in 2010.) Former National Security Adviser Michael Flynn held key intelligence positions in both Afghanistan and Iraq, while his temporary replacement (and now National Security Council chief of staff), General Joseph “Keith” Kellogg, retired and working with private contractor Oracle at the time of the invasion of Iraq, was sent to Baghdad as chief operating officer of the Coalition Provisional Authority that the Bush administration set up to run its ill-fated occupation of that country. He lasted only five months as that body began its “reconstruction” of Iraq, after disbanding Saddam’s army and so putting its officers and troops on the unemployment line, which meant at the disposal of the developing insurgency. Army Lieutenant General H.R. McMaster, the new national security adviser, just tapped for the job by Trump, isn’t even retired and held command posts in both Iraq and Afghanistan.
On the evidence of these last years, such experiences seem to have tied these men to the war against terror in a deep and visceral way, making any major reconsideration of what they had lived through inconceivable. In the new Trump era, clues to this ongoing reality can already be found in two recent events: the first Trump-ordered action in the Greater Middle East, a thoroughly botched Special Operations raid in Yemen, which did not achieve its objective but got large numbers of civilians and one Navy SEAL killed and which, given the last 15 years of U.S. military action in the region, looked painfully familiar; and the request of the present U.S. Afghan commander, General John Nicholson Jr., for “several thousand” more American military advisers, one that it’s hard to imagine he would have made before the Senate Armed Services Committee without the agreement of Defense Secretary Mattis. It’s also a request that was clearly meant as no more than an opening bid in a potentially far larger surge of American forces into Afghanistan. (Where have you heard that before?)
Under the circumstances, it’s good to know that, even if not at the highest ranks of the U.S. military, there are officers who have been able to take in what they experienced up close and personal in Iraq and Afghanistan and make some new – not desperately old – sense of it. U.S. Army Major Danny Sjursen, a former history instructor at West Point and the author of Ghostriders of Baghdad: Soldiers, Civilians, and the Myth of the Surge, who writes his inaugural TomDispatch post today, is obviously one of them and I doubt he’s alone in the American armed forces after all these years. ~ Tom
How We Got Here
The Misuse of American Military Power and The Middle East in Chaos
By Danny Sjursen
The United States has already lost – its war for the Middle East, that is. Having taken my own crack at combat soldiering in both Iraq and Afghanistan, that couldn’t be clearer to me. Unfortunately, it’s evidently still not clear in Washington. Bush’s neo-imperial triumphalism failed. Obama’s quiet shift to drones, Special Forces, and clandestine executive actions didn’t turn the tide either. For all President Trump’s bluster, boasting, and threats, rest assured that, at best, he’ll barely move the needle and, at worst… but why even go there?
At this point, it’s at least reasonable to look back and ask yet again: Why the failure? Explanations abound, of course. Perhaps Americans were simply never tough enough and still need to take off the kid gloves. Maybe there just weren’t ever enough troops. (Bring back the draft!) Maybe all those hundreds of thousands of bombs and missiles just came up short. (So how about lots more of them, maybe even a nuke?)
Lead from the front. Lead from behind. Surge yet again… The list goes on – and on and on.
And by now all of it, including Donald Trump’s recent tough talk, represents such a familiar set of tunes. But what if the problem is far deeper and more fundamental than any of that?
Here our nation stands, 15-plus years after 9/11, engaged militarily in half a dozen countries across the Greater Middle East, with no end in sight. Perhaps a more critical, factual reading of our recent past would illuminate the futility of America’s tragic, ongoing project to somehow “destroy” terrorism in the Muslim world.
The standard triumphalist version of the last 100 or so years of our history might go something like this: in the twentieth century, the United States repeatedly intervened, just in the nick of time, to save the feeble Old World from militarism, fascism, and then, in the Cold War, communism. It did indeed save the day in three global wars and might have lived happily ever after as the world’s “sole superpower” if not for the sudden emergence of a new menace. Seemingly out of nowhere, “Islamo-fascists” shattered American complacence with a sneak attack reminiscent of Pearl Harbor. Collectively the people asked: Why do they hate us? Of course, there was no time to really reflect, so the government simply got to work, taking the fight to our new “medieval” enemies on their own turf. It’s admittedly been a long, hard slog, but what choice did our leaders have? Better, after all, to fight them in Baghdad than Brooklyn.
What if, however, this foundational narrative is not just flawed but little short of delusional? Alternative accounts lead to wholly divergent conclusions and are more likely to inform prudent policy in the Middle East.
Let’s reconsider just two key years for the United States in that region: 1979 and 2003. America’s leadership learned all the wrong “lessons” from those pivotal moments and has intervened there ever since on the basis of some perverse version of them with results that have been little short of disastrous. A more honest narrative of those moments would lead to a far more modest, minimalist approach to a messy and tragic region. The problem is that there seems to be something inherently un-American about entertaining such thoughts.
1979 Revisited
Through the first half of the Cold War, the Middle East remained a sideshow. In 1979, however, all that changed radically. First, rising protests against the brutal police state of the American-backed Shah of Iran led to regime collapse, the return of dissident ayatollah Ruhollah Khomeini, and the declaration of an Islamic Republic. Then Iranian students stormed the U.S. embassy in Tehran, holding 52 hostages for more than 400 days. Of course, by then few Americans remembered the CIA-instigated coup of 1953 that had toppled a democratically elected Iranian prime minister, preserved Western oil interests in that country, and started both lands on this path (though Iranians clearly hadn’t forgotten). The shock and duration of the hostage crisis undoubtedly ensured that Jimmy Carter would be a one-term president and – to make matters worse – Soviet troops intervened in Afghanistan to shore up a communist government there. It was quite a year.
The alarmist conventional narrative of these events went like this: the radical mullahs running Iran were irrational zealots with an inexplicable loathing for the American way of life. As if in a preview of 9/11, hearing those chants against “the Great Satan,” Americans promptly began asking with true puzzlement: Why do they hate us? The hostage crisis challenged world peace. Carter had to do something. Worse yet, the Soviet invasion of Afghanistan represented blatant conquest and spotlighted the possibility of Red Army hordes pushing through to Iran en route to the Persian Gulf’s vast oil reserves. It might prove the opening act of the long awaited Soviet scheme for world domination or a possible path to World War III.
Misinformed by such a tale that they repeatedly told themselves, Washington officials then made terrible choices in the Middle East. Let’s start with Iran. They mistook a nationalist revolution and subsequent civil war within Islam for a singular attack on the U.S.A. With little consideration of genuine Iranian gripes about the brutal U.S.-backed dynasty of the Shah or the slightest appreciation for the complexity of that country’s internal dynamics, they created a simple-minded but convenient narrative in which the Iranians posed an existential threat to this country. Little has changed in almost four decades.
Then, though few Americans could locate Afghanistan on a map, most accepted that it was indeed a country of vital strategic interest. Of course, with the opening of their archives, it’s clear enough now that the Soviets never sought the worldwide empire we imagined for them, especially not by 1979. The Soviet leadership was, in fact, divided over the Afghan affair and intervened in Kabul in a spirit more defensive than aggressive. Their desire or even ability to drive towards the Persian Gulf was, at best, a fanciful American notion.
Nonetheless, the Iranian revolution and the Soviet invasion of Afghanistan were combined into a tale of horror that would lead to the permanent militarization of U.S. policy in the Middle East. Remembered today as a dove-in-chief, in his 1980 State of the Union address President Carter announced a decidedly hawkish new doctrine that would come to bear his name. From then on, he said, the U.S. would consider any threat to Persian Gulf oil supplies a direct threat to this country and American troops would, if necessary, unilaterally intervene to secure the region.
The results will seem painfully familiar today: almost immediately, Washington policymakers began to seek military solutions to virtually every problem in the Middle East. Within a year, the administration of President Ronald Reagan would, for instance, support Iraqi autocrat Saddam Hussein’s ruthless invasion of Iran, ignoring his more vicious antics and his proclivity for gassing his own people.
Soon after, in 1983, the military created the United States Central Command (headquarters: Tampa, Florida) with specific responsibility for the Greater Middle East. Its early war plans demonstrated just how wildly out of touch with reality American planners already were by then. Operational blueprints, for instance, focused on defeating Soviet armies in Iran before they could reach the Persian Gulf. Planners imagined U.S. Army divisions crossing Iran, itself in the midst of a major war with Iraq, to face off against a Soviet armored juggernaut (just like the one that was always expected to burst through Europe’s Fulda Gap). That such an assault was never coming, or that the fiercely proud Iranians might object to the militaries of either superpower crossing their territories, figured little in such early plans that were monuments to American arrogance and naïveté.
From there, it was but a few short steps to the permanent “defensive” basing of the Navy’s Fifth Fleet in Bahrain or later the stationing of U.S. troops near the holy cities of Mecca and Medina to protect Saudi Arabia from Iraqi attack. Few asked how such forces in the heart of the Middle East would play on the Arab street or corroborate Islamist narratives of “crusader” imperialism.
Worse yet, in those same years the CIA armed and financed a grab bag of Afghan insurgent groups, most of them extreme Islamists. Eager to turn Afghanistan into a Soviet “Vietnam,” no one in Washington bothered to ask whether such guerrilla outfits conformed to our purported principles or what the rebels would do if they won. Of course, the victorious guerrillas contained foreign fighters and various Arab supporters, including one Osama bin Laden. Eventually, the excesses of the well-armed but morally bankrupt insurgents and warlords in Afghanistan triggered the formation and ascension of the Taliban there, and from one of those guerrilla outfits came a new organization that called itself al-Qaeda. The rest, as they say, is history, and thanks to Chalmers Johnson’s appropriation of a classic CIA term of spy craft, we now know it as blowback.
That was a major turning point for the U.S. military. Before 1979, few of its troops had served in the region. In the ensuing decades, America bombed, invaded, raided, sent its drones to kill in, or attacked Iran, Lebanon, Libya, Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Iraq, Somalia, Afghanistan, Pakistan, Yemen, Iraq again (and again), Somalia (again and again), Libya again, Iraq once more, and now Syria as well. Before 1979, few – if any – American military personnel died in the Greater Middle East. Few have died anywhere else since.
2003 and After: Fantasies and Reality
Who wouldn’t agree that the 2003 invasion of Iraq signified a major turning point both in the history of the Greater Middle East and in our own? Nonetheless, its legacy remains highly contested. The standard narrative goes like this: as the sole remaining superpower on the planet after the implosion of the Soviet Union in 1991, our invincible military organized a swift and convincing defeat of Saddam Hussein’s Iraq in the first Gulf War. After 9/11, that same military launched an inventive, swift, and triumphant campaign in Afghanistan. Osama bin Laden escaped, of course, but his al-Qaeda network was shattered and the Taliban all but destroyed.
Naturally, the threat of Islamic terror was never limited to the Hindu Kush, so Washington “had” to take its fight against terror global. Admittedly, the subsequent conquest of Iraq didn’t exactly turn out as planned and perhaps the Arabs weren’t quite ready for American-style democracy anyway. Still, the U.S. was committed, had shed blood, and had to stay the course, rather than cede momentum to the terrorists. Anything less would have dishonored the venerated dead. Luckily, President George W. Bush found an enlightened new commander, General David Petraeus, who, with his famed “surge,” snatched victory, or at least stability, from the jaws of defeat in Iraq. He had the insurgency all but whipped. Then, just a few years later, “spineless” Barack Obama prematurely pulled American forces out of that country, an act of weakness that led directly to the rise of ISIS and the current nightmare in the region. Only a strong, assertive successor to Obama could right such gross errors.
It’s a riveting tale, of course, even if it is misguided in nearly every way imaginable. At each turn, Washington learned the wrong lessons and drew perilous conclusions. At least the first Gulf War – to George H.W. Bush’s credit – involved a large multinational coalition and checked actual Iraqi aggression. Instead of cheering Bush the Elder’s limited, prudent strategy, however, surging neoconservatives demanded to know why he had stopped short of taking the Iraqi capital, Baghdad. In these years (and for this we can certainly thank Bush, among others), Americans – Republicans and Democrats alike – became enamored with military force and came to believe that it could solve just about any problem in that region, if not the world.
This would prove a grotesque misunderstanding of what had happened. The Gulf War had been an anomaly. Triumphalist conclusions about it rested on the shakiest of foundations. Only if an enemy fought exactly as the U.S. military preferred it to do, as indeed Saddam’s forces did in 1991 – conventionally, in open desert, with outdated Soviet equipment – could the U.S. expect such success. Americans drew another conclusion entirely: that their military was unstoppable.
The same faulty assumptions flowed from Afghanistan in 2001. Information technology, Special Forces, CIA dollars (to Afghan warlords), and smart bombs triggered victory with few conventional foot soldiers needed. It seemed a forever formula and influenced both the hasty decision to invade Iraq, and the irresponsibly undersized force structure deployed (not to speak of the complete lack of serious preparation for actually occupying that country). So powerful was the optimism and jingoism of invasion proponents that skeptics were painted as unpatriotic turncoats.
Then things turned ugly fast. This time around, Saddam’s army simply melted away, state institutions broke down, looting was rampant, and the three major communities of Iraq – Sunni, Shia, and Kurd – began to battle for power. The invaders never received the jubilant welcome predicted for them by Bush administration officials and supportive neocons. What began as a Sunni-based insurgency to regain power morphed into a nationalist rebellion and then into an Islamist struggle against Westerners.
Nearly a century earlier, Britain had formed Iraq from three separate Ottoman imperial provinces – Baghdad, Basra, and Mosul. The 2003 invasion blew up that synthetic state, held together first by British overlords and then by Saddam’s brutal dictatorship. American policymakers seemed genuinely surprised by all this.
Those in Washington never adequately understood the essential conundrum of forced regime change in Iraq. “Democracy” there would inevitably result in Shia majority dominance of an artificial state. Empowering the Shia drove the Sunni minority – long accustomed to power – into the embrace of armed, motivated Islamists. When societies fracture as Iraq’s did, often enough the worst among us rise to the occasion. As the poet William Butler Yeats so famously put it, “Things fall apart; the center cannot hold; Mere anarchy is loosed upon the world, the blood-dimmed tide is loosed… The best lack all conviction, while the worst are full of passionate intensity.”
Furthermore, the invasion played directly into Osama bin Laden’s hands, fueling his narrative of an American “war on Islam.” In the process, the U.S. also destabilized Iraq’s neighbors and the region, spreading extremists to Syria and elsewhere.
That David Petraeus’s surge “worked” is perhaps the greatest myth of all. It was true that the steps he took resulted in a decrease in violence after 2007, largely because he paid off the Sunni tribes, not because of the modest U.S. troop increase ordered from Washington. By then, the Shia had already won the sectarian civil war for Baghdad, intensifying Sunni-Shia residential segregation there and so temporarily lessening the capacity for carnage.
That post-surge “calm” was, however, no more than a tactical pause in an ongoing regional sectarian war. No fundamental problems had been resolved in post-Saddam Iraq, including the nearly impossible task of integrating Sunni and Kurdish minorities into a coherent national whole. Instead, Washington had left a highly sectarian Shia strongman, Prime Minister Nouri al-Maliki, in control of the government and internal security forces, while al-Qaeda in Iraq, or AQI (nonexistent prior to the invasion), never would be eradicated. Its leadership, further radicalized in U.S. Army prisons, bided its time, waiting for an opportunity to win back Sunni fealty.
Luckily for AQI, as soon as the U.S. military was pulled out of the country, Maliki promptly cracked down hard on peaceful Sunni protests. He even had his Sunni vice president sentenced to death in absentia under the most questionable of circumstances. Maliki’s ineptitude would prove an AQI godsend.
Islamists, including AQI, also took advantage of events in Syria. Autocrat Bashar al-Assad’s brutal repression of his own protesting Sunni majority gave them just the opening they needed. Of course, the revolt there might never have occurred had not the invasion of Iraq destabilized the entire region. In 2014, the former AQI leaders, having absorbed some of Saddam’s cashiered officers into their new forces, triumphantly took a series of Iraqi cities, including Mosul, sending the Iraqi army fleeing. They then declared a caliphate in Iraq and Syria. Many Iraqi Sunnis naturally turned to the newly established “Islamic State” (ISIS) for protection.
Mission (Un)Accomplished!
It’s hardly controversial these days to point out that the 2003 invasion (aka Operation Iraqi Freedom), far from bringing freedom to that country, sowed chaos. Toppling Saddam’s brutal regime tore down the edifice of a regional system that had stood for nearly a century. However inadvertently, the U.S. military lit the fire that burned down the old order.
As it turned out, no matter the efforts of the globe’s greatest military, no easy foreign solution existed when it came to Iraq. It rarely does. Unfortunately, few in Washington were willing to accept such realities. Think of that as the twenty-first-century American Achilles’ heel: unwarranted optimism about the efficacy of U.S. power. Policy in these years might best be summarized as: “we” have to do something, and military force is the best – perhaps the only – feasible option.
Has it worked? Is anybody, including Americans, safer? Few in power even bother to ask such questions. But the data is there. The Department of State counted just 348 terrorist attacks worldwide in 2001 compared with 11,774 attacks in 2015. That’s right: at best, America’s 15-year “war on terror” failed to significantly reduce international terrorism; at worst, its actions helped make matters 30 times worse.
Recall the Hippocratic oath: “First do no harm.” And remember Osama bin Laden’s stated goal on 9/11: to draw conventional American forces into attritional campaigns in the heart of the Middle East. Mission accomplished!
In today’s world of “alternative facts,” it’s proven remarkably easy to ignore such empirical data and so avoid thorny questions. Recent events and contemporary political discourse even suggest that the country’s political elites now inhabit a post-factual environment; in terms of the Greater Middle East, this has been true for years.
It couldn’t be more obvious that Washington’s officialdom regularly and repeatedly drew erroneous lessons from the recent past and ignored a hard truth staring them in the face: U.S. military action in the Middle East has solved nothing. At all. Only the government cannot seem to accept this. Meanwhile, an American fixation on one unsuitable term – “isolationism” – masks a more apt description of American dogma in this period: hyper-interventionism.
As for military leaders, they struggle to admit failure when they – and their troops – have sacrificed so much sweat and blood in the region. Senior officers display the soldier’s tendency to confuse performance with effectiveness, staying busy with being successful. Prudent strategy requires differentiating between doing a lot and doing the right things. As Einstein reputedly opined, “Insanity is doing the same thing over and over again and expecting a different result.”
A realistic look at America’s recent past in the Greater Middle East and a humbler perspective on its global role suggest two unsatisfying but vital conclusions. First, false lessons and misbegotten collective assumptions contributed to and created much of today’s regional mess. As a result, it’s long past time to reassess recent history and challenge long-held suppositions. Second, policymakers badly overestimated the efficacy of American power, especially via the military, to shape foreign peoples and cultures to their desires. In all of this, the agency of locals and the inherent contingency of events were conveniently swept aside.
So what now? It should be obvious (but probably isn’t in Washington) that it’s well past time for the U.S. to bring its incessant urge to respond militarily to the crisis of the moment under some kind of control. Policymakers should accept realistic limitations on their ability to shape the world to America’s desired image of it.
Consider the last few decades in Iraq and Syria. In the 1990s, Washington employed economic sanctions against Saddam Hussein and his regime. The result: tragedy to the tune of half a million dead children. Then it tried invasion and democracy promotion. The result: tragedy – including 4,500-plus dead American soldiers, a few trillion dollars down the drain, more than 200,000 dead Iraqis, and millions more displaced in their own country or in flight as refugees.
In response, in Syria the U.S. tried only limited intervention. Result: tragedy – upwards of 300,000 dead and close to seven million more turned into refugees.
So will tough talk and escalated military action finally work this time around as the Trump administration faces off against ISIS? Consider what happens even if the U.S achieves a significant rollback of ISIS. Even if, in conjunction with allied Kurdish or Syrian rebel forces, ISIS’s “capital,” Raqqa, is taken and the so-called caliphate destroyed, the ideology isn’t going away. Many of its fighters are likely to transition back to an insurgency and there will be no end to international terror in ISIS’s name. In the meantime, none of this will have solved the underlying problems of artificial states now at the edge of collapse or beyond, divided ethno-religious groups, and anti-Western nationalist and religious sentiments. All of it begs the question: What if Americans are incapable of helping (at least in a military sense)?
A real course correction is undoubtedly impossible without at least a willingness to reconsider and reframe our recent historical experiences. If the 2016 election is any indication, however, a Trump administration with the present line-up of national security chiefs (who fought in these very wars) won’t meaningfully alter either the outlook or the policies that led us to this moment. Candidate Trump offered a hollow promise – to “Make America Great Again” – conjuring up a mythical era that never was. Meanwhile, Hillary Clinton offered only remarkably dated and stale rhetoric about America as the “indispensable nation.”
In the new Trump era, neither major party seems capable of escaping a shared commitment to the legends rather than the facts of America’s recent past in the Greater Middle East. Both sides remain eerily confident that the answers to contemporary foreign policy woes lie in a mythical version of that past, whether Trump’s imaginary 1950s paradise or Clinton’s fleeting mid-1990s “unipolar moment.”
Both ages are long gone, if they ever really existed at all. Needed is some fresh thinking about our militarized version of foreign policy and just maybe an urge, after all these years, to do so much less. Patriotic fables certainly feel good, but they achieve little. My advice: dare to be discomfited.
Major Danny Sjursen is a U.S. Army strategist and former history instructor at West Point. He served tours with reconnaissance units in Iraq and Afghanistan. He has written a memoir and critical analysis of the Iraq War, Ghostriders of Baghdad: Soldiers, Civilians, and the Myth of the Surge. He lives with his wife and four sons near Fort Leavenworth, Kansas.
[Note: The views expressed in this article are those of the author in an unofficial capacity and do not reflect the official policy or position of the Command and General Staff College, Department of the Army, Department of Defense, or the U.S. government.]
Follow TomDispatch on Twitter and join us on Facebook. Check out the newest Dispatch Book, John Feffer’s dystopian novel Splinterlands, as well as Nick Turse’s Next Time They’ll Come to Count the Dead, and Tom Engelhardt’s latest book, Shadow Government: Surveillance, Secret Wars, and a Global Security State in a Single-Superpower World.
Copyright 2017 Danny Sjursen
If you’re going to surround yourself with generals in the Oval Office, as Donald Trump has done, that means one thing in these years: you’re going to appoint men whose careers were made (or unmade) by what was once known as the Global War on Terror. They will be deeply associated with Washington’s 15 years of disastrous wars and conflicts in the Greater Middle East, which have left that region a set of failed or near-failed states and a hotbed of terror outfits, including various branches of al-Qaeda and the Islamic State. Secretary of Defense James “Mad Dog” Mattis, for instance, led troops in the initial post-invasion period in Afghanistan in 2001; in the taking of the Iraqi capital, Baghdad, in 2003; in the fierce fighting for the city of Fallujah in 2004; and then, from 2010 to 2013, he was in charge of U.S. Central Command (CENTCOM), with responsibility for the Greater Middle East. In that post, he cooked up a scheme to take out either an Iranian oil refinery or power plant in the “dead of night,” an act of war meant to pay that country back for supplying mortars to Iraqi insurgents killing American troops. That plan, nixed by the Obama White House, seems to have played a role in his removal from the CENTCOM post five months early.
General John Kelly, head of the Department of Homeland Security, also commanded troops and fought in Iraq. (His son was killed in Afghanistan in 2010.) Former National Security Adviser Michael Flynn held key intelligence positions in both Afghanistan and Iraq, while his temporary replacement (and now National Security Council chief of staff), General Joseph “Keith” Kellogg, retired and working with private contractor Oracle at the time of the invasion of Iraq, was sent to Baghdad as chief operating officer of the Coalition Provisional Authority that the Bush administration set up to run its ill-fated occupation of that country. He lasted only five months as that body began its “reconstruction” of Iraq, after disbanding Saddam’s army and so putting its officers and troops on the unemployment line, which meant at the disposal of the developing insurgency. Army Lieutenant General H.R. McMaster, the new national security adviser, just tapped for the job by Trump, isn’t even retired and held command posts in both Iraq and Afghanistan.
On the evidence of these last years, such experiences seem to have tied these men to the war against terror in a deep and visceral way, making any major reconsideration of what they had lived through inconceivable. In the new Trump era, clues to this ongoing reality can already be found in two recent events: the first Trump-ordered action in the Greater Middle East, a thoroughly botched Special Operations raid in Yemen, which did not achieve its objective but got large numbers of civilians and one Navy SEAL killed and which, given the last 15 years of U.S. military action in the region, looked painfully familiar; and the request of the present U.S. Afghan commander, General John Nicholson Jr., for “several thousand” more American military advisers, one that it’s hard to imagine he would have made before the Senate Armed Services Committee without the agreement of Defense Secretary Mattis. It’s also a request that was clearly meant as no more than an opening bid in a potentially far larger surge of American forces into Afghanistan. (Where have you heard that before?)
Under the circumstances, it’s good to know that, even if not at the highest ranks of the U.S. military, there are officers who have been able to take in what they experienced up close and personal in Iraq and Afghanistan and make some new – not desperately old – sense of it. U.S. Army Major Danny Sjursen, a former history instructor at West Point and the author of Ghostriders of Baghdad: Soldiers, Civilians, and the Myth of the Surge, who writes his inaugural TomDispatch post today, is obviously one of them and I doubt he’s alone in the American armed forces after all these years. ~ Tom
How We Got Here
The Misuse of American Military Power and The Middle East in Chaos
By Danny Sjursen
The United States has already lost – its war for the Middle East, that is. Having taken my own crack at combat soldiering in both Iraq and Afghanistan, that couldn’t be clearer to me. Unfortunately, it’s evidently still not clear in Washington. Bush’s neo-imperial triumphalism failed. Obama’s quiet shift to drones, Special Forces, and clandestine executive actions didn’t turn the tide either. For all President Trump’s bluster, boasting, and threats, rest assured that, at best, he’ll barely move the needle and, at worst… but why even go there?
At this point, it’s at least reasonable to look back and ask yet again: Why the failure? Explanations abound, of course. Perhaps Americans were simply never tough enough and still need to take off the kid gloves. Maybe there just weren’t ever enough troops. (Bring back the draft!) Maybe all those hundreds of thousands of bombs and missiles just came up short. (So how about lots more of them, maybe even a nuke?)
Lead from the front. Lead from behind. Surge yet again… The list goes on – and on and on.
And by now all of it, including Donald Trump’s recent tough talk, represents such a familiar set of tunes. But what if the problem is far deeper and more fundamental than any of that?
Here our nation stands, 15-plus years after 9/11, engaged militarily in half a dozen countries across the Greater Middle East, with no end in sight. Perhaps a more critical, factual reading of our recent past would illuminate the futility of America’s tragic, ongoing project to somehow “destroy” terrorism in the Muslim world.
The standard triumphalist version of the last 100 or so years of our history might go something like this: in the twentieth century, the United States repeatedly intervened, just in the nick of time, to save the feeble Old World from militarism, fascism, and then, in the Cold War, communism. It did indeed save the day in three global wars and might have lived happily ever after as the world’s “sole superpower” if not for the sudden emergence of a new menace. Seemingly out of nowhere, “Islamo-fascists” shattered American complacence with a sneak attack reminiscent of Pearl Harbor. Collectively the people asked: Why do they hate us? Of course, there was no time to really reflect, so the government simply got to work, taking the fight to our new “medieval” enemies on their own turf. It’s admittedly been a long, hard slog, but what choice did our leaders have? Better, after all, to fight them in Baghdad than Brooklyn.
What if, however, this foundational narrative is not just flawed but little short of delusional? Alternative accounts lead to wholly divergent conclusions and are more likely to inform prudent policy in the Middle East.
Let’s reconsider just two key years for the United States in that region: 1979 and 2003. America’s leadership learned all the wrong “lessons” from those pivotal moments and has intervened there ever since on the basis of some perverse version of them with results that have been little short of disastrous. A more honest narrative of those moments would lead to a far more modest, minimalist approach to a messy and tragic region. The problem is that there seems to be something inherently un-American about entertaining such thoughts.
1979 Revisited
Through the first half of the Cold War, the Middle East remained a sideshow. In 1979, however, all that changed radically. First, rising protests against the brutal police state of the American-backed Shah of Iran led to regime collapse, the return of dissident ayatollah Ruhollah Khomeini, and the declaration of an Islamic Republic. Then Iranian students stormed the U.S. embassy in Tehran, holding 52 hostages for more than 400 days. Of course, by then few Americans remembered the CIA-instigated coup of 1953 that had toppled a democratically elected Iranian prime minister, preserved Western oil interests in that country, and started both lands on this path (though Iranians clearly hadn’t forgotten). The shock and duration of the hostage crisis undoubtedly ensured that Jimmy Carter would be a one-term president and – to make matters worse – Soviet troops intervened in Afghanistan to shore up a communist government there. It was quite a year.
The alarmist conventional narrative of these events went like this: the radical mullahs running Iran were irrational zealots with an inexplicable loathing for the American way of life. As if in a preview of 9/11, hearing those chants against “the Great Satan,” Americans promptly began asking with true puzzlement: Why do they hate us? The hostage crisis challenged world peace. Carter had to do something. Worse yet, the Soviet invasion of Afghanistan represented blatant conquest and spotlighted the possibility of Red Army hordes pushing through to Iran en route to the Persian Gulf’s vast oil reserves. It might prove the opening act of the long awaited Soviet scheme for world domination or a possible path to World War III.
Misinformed by such a tale that they repeatedly told themselves, Washington officials then made terrible choices in the Middle East. Let’s start with Iran. They mistook a nationalist revolution and subsequent civil war within Islam for a singular attack on the U.S.A. With little consideration of genuine Iranian gripes about the brutal U.S.-backed dynasty of the Shah or the slightest appreciation for the complexity of that country’s internal dynamics, they created a simple-minded but convenient narrative in which the Iranians posed an existential threat to this country. Little has changed in almost four decades.
Then, though few Americans could locate Afghanistan on a map, most accepted that it was indeed a country of vital strategic interest. Of course, with the opening of their archives, it’s clear enough now that the Soviets never sought the worldwide empire we imagined for them, especially not by 1979. The Soviet leadership was, in fact, divided over the Afghan affair and intervened in Kabul in a spirit more defensive than aggressive. Their desire or even ability to drive towards the Persian Gulf was, at best, a fanciful American notion.
Nonetheless, the Iranian revolution and the Soviet invasion of Afghanistan were combined into a tale of horror that would lead to the permanent militarization of U.S. policy in the Middle East. Remembered today as a dove-in-chief, in his 1980 State of the Union address President Carter announced a decidedly hawkish new doctrine that would come to bear his name. From then on, he said, the U.S. would consider any threat to Persian Gulf oil supplies a direct threat to this country and American troops would, if necessary, unilaterally intervene to secure the region.
The results will seem painfully familiar today: almost immediately, Washington policymakers began to seek military solutions to virtually every problem in the Middle East. Within a year, the administration of President Ronald Reagan would, for instance, support Iraqi autocrat Saddam Hussein’s ruthless invasion of Iran, ignoring his more vicious antics and his proclivity for gassing his own people.
Soon after, in 1983, the military created the United States Central Command (headquarters: Tampa, Florida) with specific responsibility for the Greater Middle East. Its early war plans demonstrated just how wildly out of touch with reality American planners already were by then. Operational blueprints, for instance, focused on defeating Soviet armies in Iran before they could reach the Persian Gulf. Planners imagined U.S. Army divisions crossing Iran, itself in the midst of a major war with Iraq, to face off against a Soviet armored juggernaut (just like the one that was always expected to burst through Europe’s Fulda Gap). That such an assault was never coming, or that the fiercely proud Iranians might object to the militaries of either superpower crossing their territories, figured little in such early plans that were monuments to American arrogance and naïveté.
From there, it was but a few short steps to the permanent “defensive” basing of the Navy’s Fifth Fleet in Bahrain or later the stationing of U.S. troops near the holy cities of Mecca and Medina to protect Saudi Arabia from Iraqi attack. Few asked how such forces in the heart of the Middle East would play on the Arab street or corroborate Islamist narratives of “crusader” imperialism.
Worse yet, in those same years the CIA armed and financed a grab bag of Afghan insurgent groups, most of them extreme Islamists. Eager to turn Afghanistan into a Soviet “Vietnam,” no one in Washington bothered to ask whether such guerrilla outfits conformed to our purported principles or what the rebels would do if they won. Of course, the victorious guerrillas contained foreign fighters and various Arab supporters, including one Osama bin Laden. Eventually, the excesses of the well-armed but morally bankrupt insurgents and warlords in Afghanistan triggered the formation and ascension of the Taliban there, and from one of those guerrilla outfits came a new organization that called itself al-Qaeda. The rest, as they say, is history, and thanks to Chalmers Johnson’s appropriation of a classic CIA term of spy craft, we now know it as blowback.
That was a major turning point for the U.S. military. Before 1979, few of its troops had served in the region. In the ensuing decades, America bombed, invaded, raided, sent its drones to kill in, or attacked Iran, Lebanon, Libya, Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Iraq, Somalia, Afghanistan, Pakistan, Yemen, Iraq again (and again), Somalia (again and again), Libya again, Iraq once more, and now Syria as well. Before 1979, few – if any – American military personnel died in the Greater Middle East. Few have died anywhere else since.
2003 and After: Fantasies and Reality
Who wouldn’t agree that the 2003 invasion of Iraq signified a major turning point both in the history of the Greater Middle East and in our own? Nonetheless, its legacy remains highly contested. The standard narrative goes like this: as the sole remaining superpower on the planet after the implosion of the Soviet Union in 1991, our invincible military organized a swift and convincing defeat of Saddam Hussein’s Iraq in the first Gulf War. After 9/11, that same military launched an inventive, swift, and triumphant campaign in Afghanistan. Osama bin Laden escaped, of course, but his al-Qaeda network was shattered and the Taliban all but destroyed.
Naturally, the threat of Islamic terror was never limited to the Hindu Kush, so Washington “had” to take its fight against terror global. Admittedly, the subsequent conquest of Iraq didn’t exactly turn out as planned and perhaps the Arabs weren’t quite ready for American-style democracy anyway. Still, the U.S. was committed, had shed blood, and had to stay the course, rather than cede momentum to the terrorists. Anything less would have dishonored the venerated dead. Luckily, President George W. Bush found an enlightened new commander, General David Petraeus, who, with his famed “surge,” snatched victory, or at least stability, from the jaws of defeat in Iraq. He had the insurgency all but whipped. Then, just a few years later, “spineless” Barack Obama prematurely pulled American forces out of that country, an act of weakness that led directly to the rise of ISIS and the current nightmare in the region. Only a strong, assertive successor to Obama could right such gross errors.
It’s a riveting tale, of course, even if it is misguided in nearly every way imaginable. At each turn, Washington learned the wrong lessons and drew perilous conclusions. At least the first Gulf War – to George H.W. Bush’s credit – involved a large multinational coalition and checked actual Iraqi aggression. Instead of cheering Bush the Elder’s limited, prudent strategy, however, surging neoconservatives demanded to know why he had stopped short of taking the Iraqi capital, Baghdad. In these years (and for this we can certainly thank Bush, among others), Americans – Republicans and Democrats alike – became enamored with military force and came to believe that it could solve just about any problem in that region, if not the world.
This would prove a grotesque misunderstanding of what had happened. The Gulf War had been an anomaly. Triumphalist conclusions about it rested on the shakiest of foundations. Only if an enemy fought exactly as the U.S. military preferred it to do, as indeed Saddam’s forces did in 1991 – conventionally, in open desert, with outdated Soviet equipment – could the U.S. expect such success. Americans drew another conclusion entirely: that their military was unstoppable.
The same faulty assumptions flowed from Afghanistan in 2001. Information technology, Special Forces, CIA dollars (to Afghan warlords), and smart bombs triggered victory with few conventional foot soldiers needed. It seemed a forever formula and influenced both the hasty decision to invade Iraq, and the irresponsibly undersized force structure deployed (not to speak of the complete lack of serious preparation for actually occupying that country). So powerful was the optimism and jingoism of invasion proponents that skeptics were painted as unpatriotic turncoats.
Then things turned ugly fast. This time around, Saddam’s army simply melted away, state institutions broke down, looting was rampant, and the three major communities of Iraq – Sunni, Shia, and Kurd – began to battle for power. The invaders never received the jubilant welcome predicted for them by Bush administration officials and supportive neocons. What began as a Sunni-based insurgency to regain power morphed into a nationalist rebellion and then into an Islamist struggle against Westerners.
Nearly a century earlier, Britain had formed Iraq from three separate Ottoman imperial provinces – Baghdad, Basra, and Mosul. The 2003 invasion blew up that synthetic state, held together first by British overlords and then by Saddam’s brutal dictatorship. American policymakers seemed genuinely surprised by all this.
Those in Washington never adequately understood the essential conundrum of forced regime change in Iraq. “Democracy” there would inevitably result in Shia majority dominance of an artificial state. Empowering the Shia drove the Sunni minority – long accustomed to power – into the embrace of armed, motivated Islamists. When societies fracture as Iraq’s did, often enough the worst among us rise to the occasion. As the poet William Butler Yeats so famously put it, “Things fall apart; the center cannot hold; Mere anarchy is loosed upon the world, the blood-dimmed tide is loosed… The best lack all conviction, while the worst are full of passionate intensity.”
Furthermore, the invasion played directly into Osama bin Laden’s hands, fueling his narrative of an American “war on Islam.” In the process, the U.S. also destabilized Iraq’s neighbors and the region, spreading extremists to Syria and elsewhere.
That David Petraeus’s surge “worked” is perhaps the greatest myth of all. It was true that the steps he took resulted in a decrease in violence after 2007, largely because he paid off the Sunni tribes, not because of the modest U.S. troop increase ordered from Washington. By then, the Shia had already won the sectarian civil war for Baghdad, intensifying Sunni-Shia residential segregation there and so temporarily lessening the capacity for carnage.
That post-surge “calm” was, however, no more than a tactical pause in an ongoing regional sectarian war. No fundamental problems had been resolved in post-Saddam Iraq, including the nearly impossible task of integrating Sunni and Kurdish minorities into a coherent national whole. Instead, Washington had left a highly sectarian Shia strongman, Prime Minister Nouri al-Maliki, in control of the government and internal security forces, while al-Qaeda in Iraq, or AQI (nonexistent prior to the invasion), never would be eradicated. Its leadership, further radicalized in U.S. Army prisons, bided its time, waiting for an opportunity to win back Sunni fealty.
Luckily for AQI, as soon as the U.S. military was pulled out of the country, Maliki promptly cracked down hard on peaceful Sunni protests. He even had his Sunni vice president sentenced to death in absentia under the most questionable of circumstances. Maliki’s ineptitude would prove an AQI godsend.
Islamists, including AQI, also took advantage of events in Syria. Autocrat Bashar al-Assad’s brutal repression of his own protesting Sunni majority gave them just the opening they needed. Of course, the revolt there might never have occurred had not the invasion of Iraq destabilized the entire region. In 2014, the former AQI leaders, having absorbed some of Saddam’s cashiered officers into their new forces, triumphantly took a series of Iraqi cities, including Mosul, sending the Iraqi army fleeing. They then declared a caliphate in Iraq and Syria. Many Iraqi Sunnis naturally turned to the newly established “Islamic State” (ISIS) for protection.
Mission (Un)Accomplished!
It’s hardly controversial these days to point out that the 2003 invasion (aka Operation Iraqi Freedom), far from bringing freedom to that country, sowed chaos. Toppling Saddam’s brutal regime tore down the edifice of a regional system that had stood for nearly a century. However inadvertently, the U.S. military lit the fire that burned down the old order.
As it turned out, no matter the efforts of the globe’s greatest military, no easy foreign solution existed when it came to Iraq. It rarely does. Unfortunately, few in Washington were willing to accept such realities. Think of that as the twenty-first-century American Achilles’ heel: unwarranted optimism about the efficacy of U.S. power. Policy in these years might best be summarized as: “we” have to do something, and military force is the best – perhaps the only – feasible option.
Has it worked? Is anybody, including Americans, safer? Few in power even bother to ask such questions. But the data is there. The Department of State counted just 348 terrorist attacks worldwide in 2001 compared with 11,774 attacks in 2015. That’s right: at best, America’s 15-year “war on terror” failed to significantly reduce international terrorism; at worst, its actions helped make matters 30 times worse.
Recall the Hippocratic oath: “First do no harm.” And remember Osama bin Laden’s stated goal on 9/11: to draw conventional American forces into attritional campaigns in the heart of the Middle East. Mission accomplished!
In today’s world of “alternative facts,” it’s proven remarkably easy to ignore such empirical data and so avoid thorny questions. Recent events and contemporary political discourse even suggest that the country’s political elites now inhabit a post-factual environment; in terms of the Greater Middle East, this has been true for years.
It couldn’t be more obvious that Washington’s officialdom regularly and repeatedly drew erroneous lessons from the recent past and ignored a hard truth staring them in the face: U.S. military action in the Middle East has solved nothing. At all. Only the government cannot seem to accept this. Meanwhile, an American fixation on one unsuitable term – “isolationism” – masks a more apt description of American dogma in this period: hyper-interventionism.
As for military leaders, they struggle to admit failure when they – and their troops – have sacrificed so much sweat and blood in the region. Senior officers display the soldier’s tendency to confuse performance with effectiveness, staying busy with being successful. Prudent strategy requires differentiating between doing a lot and doing the right things. As Einstein reputedly opined, “Insanity is doing the same thing over and over again and expecting a different result.”
A realistic look at America’s recent past in the Greater Middle East and a humbler perspective on its global role suggest two unsatisfying but vital conclusions. First, false lessons and misbegotten collective assumptions contributed to and created much of today’s regional mess. As a result, it’s long past time to reassess recent history and challenge long-held suppositions. Second, policymakers badly overestimated the efficacy of American power, especially via the military, to shape foreign peoples and cultures to their desires. In all of this, the agency of locals and the inherent contingency of events were conveniently swept aside.
So what now? It should be obvious (but probably isn’t in Washington) that it’s well past time for the U.S. to bring its incessant urge to respond militarily to the crisis of the moment under some kind of control. Policymakers should accept realistic limitations on their ability to shape the world to America’s desired image of it.
Consider the last few decades in Iraq and Syria. In the 1990s, Washington employed economic sanctions against Saddam Hussein and his regime. The result: tragedy to the tune of half a million dead children. Then it tried invasion and democracy promotion. The result: tragedy – including 4,500-plus dead American soldiers, a few trillion dollars down the drain, more than 200,000 dead Iraqis, and millions more displaced in their own country or in flight as refugees.
In response, in Syria the U.S. tried only limited intervention. Result: tragedy – upwards of 300,000 dead and close to seven million more turned into refugees.
So will tough talk and escalated military action finally work this time around as the Trump administration faces off against ISIS? Consider what happens even if the U.S achieves a significant rollback of ISIS. Even if, in conjunction with allied Kurdish or Syrian rebel forces, ISIS’s “capital,” Raqqa, is taken and the so-called caliphate destroyed, the ideology isn’t going away. Many of its fighters are likely to transition back to an insurgency and there will be no end to international terror in ISIS’s name. In the meantime, none of this will have solved the underlying problems of artificial states now at the edge of collapse or beyond, divided ethno-religious groups, and anti-Western nationalist and religious sentiments. All of it begs the question: What if Americans are incapable of helping (at least in a military sense)?
A real course correction is undoubtedly impossible without at least a willingness to reconsider and reframe our recent historical experiences. If the 2016 election is any indication, however, a Trump administration with the present line-up of national security chiefs (who fought in these very wars) won’t meaningfully alter either the outlook or the policies that led us to this moment. Candidate Trump offered a hollow promise – to “Make America Great Again” – conjuring up a mythical era that never was. Meanwhile, Hillary Clinton offered only remarkably dated and stale rhetoric about America as the “indispensable nation.”
In the new Trump era, neither major party seems capable of escaping a shared commitment to the legends rather than the facts of America’s recent past in the Greater Middle East. Both sides remain eerily confident that the answers to contemporary foreign policy woes lie in a mythical version of that past, whether Trump’s imaginary 1950s paradise or Clinton’s fleeting mid-1990s “unipolar moment.”
Both ages are long gone, if they ever really existed at all. Needed is some fresh thinking about our militarized version of foreign policy and just maybe an urge, after all these years, to do so much less. Patriotic fables certainly feel good, but they achieve little. My advice: dare to be discomfited.
Major Danny Sjursen is a U.S. Army strategist and former history instructor at West Point. He served tours with reconnaissance units in Iraq and Afghanistan. He has written a memoir and critical analysis of the Iraq War, Ghostriders of Baghdad: Soldiers, Civilians, and the Myth of the Surge. He lives with his wife and four sons near Fort Leavenworth, Kansas.
[Note: The views expressed in this article are those of the author in an unofficial capacity and do not reflect the official policy or position of the Command and General Staff College, Department of the Army, Department of Defense, or the U.S. government.]
Follow TomDispatch on Twitter and join us on Facebook. Check out the newest Dispatch Book, John Feffer’s dystopian novel Splinterlands, as well as Nick Turse’s Next Time They’ll Come to Count the Dead, and Tom Engelhardt’s latest book, Shadow Government: Surveillance, Secret Wars, and a Global Security State in a Single-Superpower World.
Copyright 2017 Danny Sjursen
Read more by Tom Engelhardt
- The Honeymoon of the Generals – April 23rd, 2017
- From Deterrence to Doomsday? – April 13th, 2017
- Alaska in the Crosshairs – April 9th, 2017
- Believe the Autocrat – April 6th, 2017
- The Teflon Wars – April 4th, 2017
 An editor in publishing for the last 25 years, Tom Engelhardt is the author of The End of Victory Culture, a history of American triumphalism in the Cold War era, now out in a revised edition with a new preface and afterword, and Mission Unaccomplished, TomDispatch Interviews With American Iconoclasts and Dissenters. He is at present consulting editor for Metropolitan Books, a fellow of the Nation Institute, and a teaching fellow at the journalism school of the University of California, Berkeley. Visit his Web site.
An editor in publishing for the last 25 years, Tom Engelhardt is the author of The End of Victory Culture, a history of American triumphalism in the Cold War era, now out in a revised edition with a new preface and afterword, and Mission Unaccomplished, TomDispatch Interviews With American Iconoclasts and Dissenters. He is at present consulting editor for Metropolitan Books, a fellow of the Nation Institute, and a teaching fellow at the journalism school of the University of California, Berkeley. Visit his Web site.
This article originally appeared at TomDispatch.com. To stay on top of important articles like these, sign up to receive the latest updates from TomDispatch.com.

Full archives
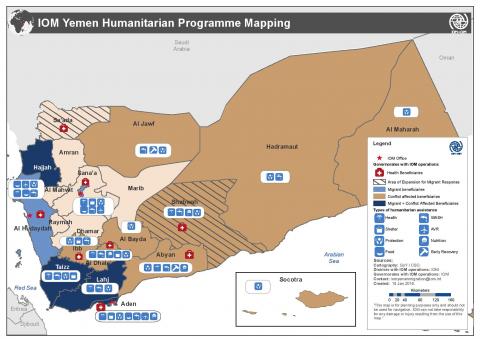
Humanitarian Catastrophe Looms in Yemen with Over 3.3 Million Displaced Since Crisis Began

Posted:
04/25/17
Region-Country:
Africa and Middle East / Yemen
Themes:
Humanitarian Emergencies, Internally Displaced Persons
Yemen - Yemen has become the world’s largest humanitarian crisis. In total, 18.8 million people need humanitarian or protection assistance. Since 2015, of the 3.3 million people who have been forced to flee their homes to seek safety, two million remain displaced and nearly 1.3 million have returned to the governorates they originated from. With no end in sight for the conflict, displacement is set to continue to increase.
Today (25 April), the United Nations and the governments of Switzerland and Sweden host a High-level Pledging Event in Geneva, Switzerland, for the Humanitarian Crisis in Yemen. Laura Thompson, the Deputy Director General of the UN Migration Agency, is attending this event.
“We cannot close our eyes to the mobility dimensions of this crisis. IOM has, since the escalation of violence in 2015, scaled up its response in Yemen to assist displaced populations and host communities,” said Ambassador Thompson. “In 2017, IOM is committed to doing more and will continue to deliver life-saving humanitarian aid, with a specific focus on the immediate and longer-term needs of migrants, internally displaced persons (IDPs) and the conflict and natural disaster affected communities in Yemen,” she continued.
Years of poverty, underdevelopment, environmental decline, intermittent conflict, and weak rule of law – including widespread violations of human rights – have contributed to over five years of crisis. The breakdown of basic services and institutions, such as hospitals, galloping poverty, environmental decline and collapse of the agricultural sector have all further compounded the situation. The conflict and its economic consequences are also driving a food crisis. Over 17 million people are currently food insecure, of whom 6.8 million require immediate food assistance.
The crisis in Yemen is not only characterized by conflict but also by natural disaster-induced large-scale displacement and complex external migration flows and mobility patterns.
Yemen has a complex migratory status, as a country of origin, transit, and destination. Regular migration flows between the Horn of Africa and Yemen have surged, with 10,000 migrants entering the country each month, as a result of the complex realities of political and economic dynamics in the region. The number of migrants has overwhelmed available resources. In addition to those staying in Yemen, many migrants transit under alarming conditions through war-torn Yemen to Saudi Arabia in search of work, and are often victims of smuggling rings and other criminal networks.
The co-hosts and participants in the High-Level Pledging Event aim to avert a humanitarian catastrophe by raising USD 2.1 billion needed to deliver crucial food, nutrition, health and other lifesaving assistance in Yemen.
As part of the inter-agency humanitarian response plan, IOM is seeking USD 76.3 million in funding to carry out migrant assistance and protection, child protection, shelter support, water and sanitation activities, health and mental health support, food assistance, displacement tracking, efforts to combat gender-based violence and victim support and early recovery activities. IOM has the highest coverage of any UN organization in Yemen with operations in 20 of the 22 governorates and over 600 staff. Read IOM’s strategy for Yemen 2017-2018 here.
“We therefore commit and call on partners to unite behind a holistic and robust humanitarian response; for governments to support and commit to political dialogue towards ending this crisis, and for the parties to the conflict to facilitate immediate, timely and unimpeded humanitarian access,” continued Ambassador Thompson. “More needs to be done before the situation in Yemen reaches a point of no return,” she concluded.
For further information, please contact Laurent de Boeck, IOM Yemen, Tel: +967 736 777 915, Email: ldeboeck@iom.int or Olivia Headon at IOM HQ, Tel: +41 79 403 53 65, Email: oheadon@iom.int
IOM Supports Introduction of Drought Resistant Potato in Somalia
Posted:
02/24/17
Region-Country:
Africa and Middle East / Somalia
Themes:
Humanitarian Emergencies, Internally Displaced Persons
Somalia
- IOM, in partnership with the Rural Education and Agriculture
Development Organization (READO), a local NGO, is introducing a drought
resistant variant of sweet potatoes which will help mitigate the impact
of drought in Somalia. The latest drought period has left over 6.2
million people in need of humanitarian assistance.
The project mainly targets internally displaced persons (IDPs) and the host community in Baidoa, who will be trained on how to grow the potatoes, before being issued with a set of vines that they can use on their own farms. This sweet potato variant, commonly referred to as the orange flesh sweet potato (OFSP), is suitable for growth in regions with minimal rainfall.
Additionally, the OFSP is nutrient rich in Vitamin A and will help boost nutrition among malnourished children and within IDP households. OFSP’s other benefits include increasing milk production among breast feeding mothers, OFSP flour to make baked products, and the plant’s edible leaves that can be consumed as vegetables and serve as fodder for livestock.
“The introduction of OFSP in Baidoa will be of great value to the community as it will help to improve the livelihood of IDPs. We urge other international organizations and local partners to support the initiative, as this will help in mitigating drought issues in Somalia,” said Abdullahi Abdirahman Ali, READO Executive Director.
Since 2011, IOM Somalia has been working with different stakeholders in Somalia to address food security and durable solutions. Some notable projects to this end include agricultural farm inputs distributions, training on best agricultural farm practices, and provision of conditional and unconditional cash for work.
For further information, please contact IOM Somalia. Omar Kharye, Tel: +254 708 985 812 Email: okhayre@iom.int, or Abubakar Ibrahim Tel +254 720 736 432 Email: aibrahim@iom.int
The project mainly targets internally displaced persons (IDPs) and the host community in Baidoa, who will be trained on how to grow the potatoes, before being issued with a set of vines that they can use on their own farms. This sweet potato variant, commonly referred to as the orange flesh sweet potato (OFSP), is suitable for growth in regions with minimal rainfall.
Additionally, the OFSP is nutrient rich in Vitamin A and will help boost nutrition among malnourished children and within IDP households. OFSP’s other benefits include increasing milk production among breast feeding mothers, OFSP flour to make baked products, and the plant’s edible leaves that can be consumed as vegetables and serve as fodder for livestock.
“The introduction of OFSP in Baidoa will be of great value to the community as it will help to improve the livelihood of IDPs. We urge other international organizations and local partners to support the initiative, as this will help in mitigating drought issues in Somalia,” said Abdullahi Abdirahman Ali, READO Executive Director.
Since 2011, IOM Somalia has been working with different stakeholders in Somalia to address food security and durable solutions. Some notable projects to this end include agricultural farm inputs distributions, training on best agricultural farm practices, and provision of conditional and unconditional cash for work.
For further information, please contact IOM Somalia. Omar Kharye, Tel: +254 708 985 812 Email: okhayre@iom.int, or Abubakar Ibrahim Tel +254 720 736 432 Email: aibrahim@iom.int
Douglas Todd: Pedophilia sets off alarms. Here are the facts

Published on: February 25, 2017 | Last Updated: February 27, 2017 8:32 AM PDT

These are some of the hundreds of movies and TV series that have revolved around the disturbing subject of child sexual abuse.
Until the 1960s, the molestation of minors was a reality that existed largely under the radar.
But since then the West has become painfully aware of this form of sexual abuse through waves of news reports, including this week’s media storm over the resignation of Breitbart News editor Milo Yiannopoulos amid a backlash over comments he made that appeared to condone sex with 13-year-olds.
It turns out what we don’t know about pedophilia could hurt us as a society. We may be missing opportunities to prevent further abuse.
Researchers generally report that roughly 20 per cent of females and 10 per cent of males worldwide have at some time experienced sexual contact between an adult and a child.
While some who have such experiences go on to enjoy vibrant lives, others succumb to mental and physical problems, addiction, revictimization, criminality and disrupted relationships.

Most are not aware of key developments that could lead to better ways to reduce these sex crimes.
Four facts:
1. A tiny fraction of people appear hard-wired for what psychologists call “pedophilic interests.”
2. Most people with sustained pedophilic desires feel deeply ashamed.
3. Child-abuse rates are significantly declining. Recidivism is low.
4. A cutting-edge approach has been developed that can prevent people with pedophilic impulses from ever abusing.
We need a fuller picture of the disorder of pedophilia if we hope to stop abuse.
After graduating with a PhD from Simon Fraser University, Vancouver psychologist Anton Schweighofer became involved in forensic work with Correctional Services Canada, which led to him developing a sub-specialty in the prevention of sexual violence, focusing on northern B.C.
In the past 20 years Schweighofer has become well aware of the one per cent of the population, mostly males, with pedophilic interests, which means they feel intense sexual attraction over an extended period to pre-pubescent and (some therapists add) pubescent youngsters.
The latest research, including by psychologist James Cantor of the University of Toronto, strongly suggests the brains of some people are hard-wired for pedophilia, Schweighofer says. Some “soft” biological signs of it include shortness and left-handedness.
Most realize in their teens and twenties they are strongly sexually attracted to children, he says. The relatively small proportion who offend usually do so in their younger years, most often with someone they know.
There is only a very small chance of males in their sixties acting out a pedophilic impulse. The “dirty old man” label is misleading.
And most pedophilic individuals feel humiliation, explains Schweighofer.
“They say they’ve got this interest in minors. And they’re so ashamed. And they want to deal with it so it doesn’t go anywhere.”
Contrary to the impression left by the mass media, the rates of child sexual abuse have also been declining.
Various forms of child abuse and molestation have plummeted by 40 to 70 per cent in Canada and the U.S. since the early 1990s, report American researchers David Finkelhor and Lisa Jones.
Why? Schweighofer joins Finkelhor and Jones in saying multiple factors explain the drop — including increased prosecution, therapy programs for offenders, general awareness, victim treatment, enhanced background checks, the “wanted child” effect and demographic shifts.
In general, Schweighofer says it’s important to recognize “not all people who molest children are pedophiles and not all pedophilic individuals go on to abuse children.”
However, he says people with pedophilia are somewhat more likely to reoffend. The rate of recidivism is about 21 per cent, for instance, for pedophilic individuals who abuse minors of the same sex.
The people with pedophilic interests who are most likely to offend are those who have anti-social tendencies or other sexually deviant interests.
Those least likely to abuse children, Schweighofer says, are those who are also sexually attracted to adults, who have “decent intimacy skills” and an ability to control their impulses.

Working in correctional settings and around the province, Schweighofer is among those periodically asked to provide mandatory treatment to pedophiles who have been incarcerated.‘Why not try to identify those with pedophilia before they offend? There’s huge potential to reduce the cost to society’ — Anton Schweighofer
Their treatment regimen, which typically involves the proven methods of cognitive-behavioural therapy (CBT) and sometimes medication, is provided at no cost.
And it’s effective, as suggested by the relatively low recidivism stats.
So why, Schweighofer asks, do most Canadian and U.S. governments wait until pedophiles abuse a child to provide free therapy?
“The violence has already occurred. Friends and family have been affected. Why not try to identify those with pedophilia before they offend? There’s huge potential to reduce the cost to society.”
In two decades of practice, Schweighofer says only one or two people with pedophilic interests who have not offended have come to him on their own.
“Pedophilia is such a stigmatized condition that few feel able to seek out treatment with a private therapist, or if they want it, it is cost prohibitive. A psychologist with expertise is expensive.”
Related
- Douglas Todd: Movie shines a ‘Spotlight’ on corruption
- Douglas Todd: Free therapy is just good economics
- Hyper-vigilance about abuse can hurt children - and everyone
- Milo Yiannopoulos resigns as editor of Breitbart Tech after video appears to show him endorsing pedophilia
One notable prevention effort out of Berlin is called Dunkelfeld, which literally translates as “dark field.”
The Dunkelfeld Prevention Project has posted notices in public spaces in Europe to draw the attention of people sexually attracted to minors.
“Do you like children more than you/they like?” asks one Dunkelfeld sign.
“You are not guilty because of your sexual desire, but you are responsible for your sexual behaviour. There is help! Don’t become an offender!’ says other Dunkelfeld material.
The Dunkelfeld campaign has attracted thousands of people for treatment, mostly those who admit they are sexually attracted to minors but have never acted on it.
(The legalities are complex, however. German privacy laws protect those with pedophilic interests from being automatically reported to authorities. But reporting rules vary elsewhere. In some U.S. jurisdictions the justice system is so hyper-vigilant that someone with pedophilic interests would never admit them to a therapist for the justified fear of being sent to jail.)
Versions of the Dunkelfeld Prevention Project are now being tried with success in Britain, the Netherlands and Belgium.
And a self-help variation also exists in North America through a website called the Virtuous Pedophile, whose members are people with pedophilic interests who are committed to never acting on them.
Schweighofer is convinced Germany’s Dunkelfeld Prevention Project is a model for Canada. “We’ve had enough of being tough on crime,” he says. “We need to be smart on crime.”
Of all the distressing movies and TV series built on sexual abuse, one that stands out for Schweighofer is The Woodsman. In it Kevin Bacon plays a man who returns to his hometown after being convicted of molesting a child.
Bacon’s character realistically conveys the confusion and guilt of someone who knows he can shatter innocent lives. The Woodsman makes it clear, Schweighofer said, the condition of pedophilia “is not something you would wish on your worst enemy.”
With better understanding of this difficult subject, society could do more to prevent those harbouring pedophilic interests from ever abusing.
dtodd@postmedia.com
Twitter.com/douglastodd
Blog: The Search
MORE RELATED: B.C.’s domestic violence approach based on ‘false theory’
CLICK HERE to report a typo.
Is there more to this story? We’d like to hear from you about this or any other stories you think we should know about. Email vantips@postmedia.com.
Read more: http://vancouversun.com/opinion/columnists/douglas-todd-pedophilia-and-how-what-we-dont-know-about-it-further-hurts-us
Letter: Speaking out is only way to stop child abuse
To the Editor:
The DeKalb County community needs to be applauded. It is in times of tragedy that everyone comes together, and that has certainly happened in recent months.
We are well-versed in the prevalence of child abuse in our community. It seems that we see an arrest, plea, conviction or sentencing in our newspaper a couple of times a week lately.
I am so proud of community members for reaching out to the Children’s Advocacy Center and asking what signs to watch for in regard to child abuse, how they can talk to their children, what they should do if they suspect abuse or if they hear a disclosure of abuse.
Children must be taught the value of boundaries and the importance of safe relationships. Adults must be vigilant in recognizing the signs and must report suspected abuse to local law enforcement and to child protection.
It is very common for people to believe that in order to report suspected abuse, there must be proof. That is false. If you have a disclosure from a child, that is all you need. If you have a reasonable suspicion, that is all you need.
If you meet one of those criteria, please call 800-25-ABUSE and/or local law enforcement.
It is imperative that we shatter the silence of abuse. Not talking about it does not make it go away. The sexual abuse of a child is not something that will simply stop happening, it will continue until the silence is broken.
Healing begins with reporting the abuse so that children and their caregivers can be connected with the resources that they need.
The Children’s Advocacy Center works closely with licensed and certified trauma clinicians. Child abuse is a community issue, and I promise that we can make a difference in the lives of children, together.
Holly Ann Peifer
Director of Children’s Advocacy Center
Read more: http://www.daily-chronicle.com/2017/02/21/letter-speaking-out-is-only-way-to-stop-child-abuse/aebxy7k/
DeKalb
The DeKalb County community needs to be applauded. It is in times of tragedy that everyone comes together, and that has certainly happened in recent months.
We are well-versed in the prevalence of child abuse in our community. It seems that we see an arrest, plea, conviction or sentencing in our newspaper a couple of times a week lately.
I am so proud of community members for reaching out to the Children’s Advocacy Center and asking what signs to watch for in regard to child abuse, how they can talk to their children, what they should do if they suspect abuse or if they hear a disclosure of abuse.
Children must be taught the value of boundaries and the importance of safe relationships. Adults must be vigilant in recognizing the signs and must report suspected abuse to local law enforcement and to child protection.
It is very common for people to believe that in order to report suspected abuse, there must be proof. That is false. If you have a disclosure from a child, that is all you need. If you have a reasonable suspicion, that is all you need.
If you meet one of those criteria, please call 800-25-ABUSE and/or local law enforcement.
It is imperative that we shatter the silence of abuse. Not talking about it does not make it go away. The sexual abuse of a child is not something that will simply stop happening, it will continue until the silence is broken.
Healing begins with reporting the abuse so that children and their caregivers can be connected with the resources that they need.
The Children’s Advocacy Center works closely with licensed and certified trauma clinicians. Child abuse is a community issue, and I promise that we can make a difference in the lives of children, together.
Holly Ann Peifer
Director of Children’s Advocacy Center
Read more: http://www.daily-chronicle.com/2017/02/21/letter-speaking-out-is-only-way-to-stop-child-abuse/aebxy7k/
DeKalb
Saturday, April 22, 2017
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)